Enormous use of cloud on public, private and community networks are making the security and compliance issues to be resolved on the highest priority. According to Gartner survey report in 2015, following graph depict the security concerns for cloud. Users are not aware about who is accessing their data and applications and how much secure, is the CSP provider. On the multitenant services, the data can be hacked and viewed by competitors. SaaS security covers, “application discovery” which will discover all the applications on the single network and provide visibility for risk factors involved. In SaaS, applications are deployed and managed at the CSP provider’s datacenter. These services are paid with subscriptions and are accessible over the net. Customer can get the license for the services on demand for example: Salesforce.com CRM application is a SaaS based app. Virtualization is one of the major component of cloud, having number of different instances running on the same server and isolated from each other, which is the main concern of security. Local users can bypass few specific security restrictions to gain authority over virtualization. Therefore, the CSPs has to revise the scenarios in depth with all the compliance guidelines under SaaS. Following image outlined the security issues in SaaS.
Users are not aware about who is accessing their data and applications and how much secure, is the CSP provider. On the multitenant services, the data can be hacked and viewed by competitors. SaaS security covers, “application discovery” which will discover all the applications on the single network and provide visibility for risk factors involved. In SaaS, applications are deployed and managed at the CSP provider’s datacenter. These services are paid with subscriptions and are accessible over the net. Customer can get the license for the services on demand for example: Salesforce.com CRM application is a SaaS based app. Virtualization is one of the major component of cloud, having number of different instances running on the same server and isolated from each other, which is the main concern of security. Local users can bypass few specific security restrictions to gain authority over virtualization. Therefore, the CSPs has to revise the scenarios in depth with all the compliance guidelines under SaaS. Following image outlined the security issues in SaaS.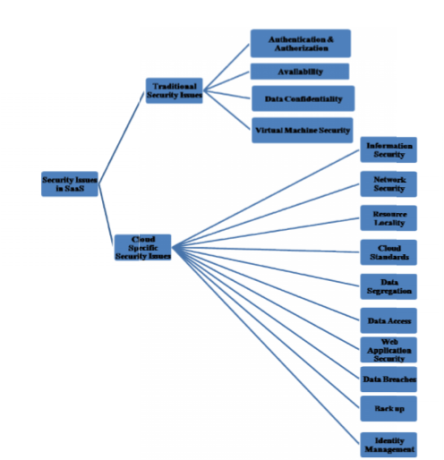
SaaS applications require an architecture, which has security mapping in its core with capabilities of multiple concurrent procedures, resource isolation for data security through isolation of virtual and hypervisor cache. SaaS architecture use, Identity and access management to further synchronize the process for authentication and authorization with application control mechanism. Data isolation and resource localization among the distributed architecture with authentication controls over a secured network is the base for a simplified, secured environment on cloud.
Current Solutions available for securing application infrastructure in SaaS:
| Security Areas | Solutions with SaaS |
| Authentication and authorization | ·Open authorization
·Two Factor Authentication OAUTCH Security in SaaS Connectors (OAuth 1.0 protocol is an international standard authentication method developed by the Open API.) User – A personal account to use the Service Provider. Consumer – OAuth Service Provider to access the web site or application Service Provider – Web applications to support access via OAuth.
|
| Availability | ·Data Dispersion |
| Data confidentiality | ·Attribute based Proxy Re-Encryption |
| Virtual Machine Security | • Reconfigurable distributed virtual machine
• Survey on Virtual machine Security |
| Information Security | • Information Security Risk Management Framework |
| Network Security | • Network Security for virtual machines • Network Security Sandbox |
| Cloud standards | • IEEE Cloud Computing Standard Study Group
• ITU Cloud Computing Focus Group • Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) |
| Data Access | • Multi-user access policies
• Data Access Management |
| Web application security | • Web Application Scanners |
| Data breaches | |
| Backup | • Agentless Method for data Backup and Recovery |
| Identity management and sign-on process | • CSA’s Identity and Access Management Guidance |
In SaaS, Microsoft provide an operational and secured infrastructure with multiple host environments including different application layers. Data transaction is secured with network protocols between Microsoft and the customer. User can control and secure data and can identify and configure the set of application controls with the cloud services. Microsoft provide enterprise cloud services with comprehensive tactics, including data and information processing over physical storage and datacenters. Microsoft has clearly defined the customer responsibilities and role in the security management of data and information. Following are some best security models, which can enhance the security and compliance for your applications under SaaS.
- Identity and access management to use across Azure and other services such as Office 365,to process efficiently over distributed farms and environment and to control user access for all the applications.
- Azure Active Directory, provide a controlled access management for data and information over Azure, Office 365 and other application on cloud.
- Multi-Factor Authentication and access monitoring offers heightened security mechanism.
- Azure Key Vault – use of cryptographic keys and other secrets used by cloud apps and services(Microsoft do not use or extract your keys)
- “Third- party” SaaS identity control management – Single sign-on and integration provided by Azure Ad enables a secured access of applications over SaaS, such as Salesforce.
- Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) – use different encryption key for each connection, to protect access of system, through hackers.
- Data at rest – SaaS services use encryption at rest to protect your data on Microsoft servers and datacenters.
- Privacy reviews – As a part of process and documentation, privacy reviews are organized to verify that privacy requirements are adequately addressed. It will allow the customer to control the information and data for their application and executing user management for who can access the application to meet all the regulatory security guidelines.
- Customer Data use – Microsoft services do not use the customer data for advertising and provide “No Standing Access policy” to access the customer data by any Microsoft personnel, it can be used for support and operations related and then can be revoked when no longer required.
- Data ownership – All the data including all text, sound, software, or image files, provided by the customer is solely related to the customer.
- Operational Security for Online Services (OSA) – OSA is used as a framework to focus on infrastructure related issues to help and protect “system and operations” throughout the lifecycle of cloud-based services.
- Private connection – All the applications can use “ExpressRoute” to establish a private connection to Azure datacenters, keeping their traffic and access off the Internet.
- Incident management – used, to alleviate the effects of attacks and malicious activities for the system. Procedural incident management is guided among the team for all the communication and recovery, and use of discoverable and predictable interfaces is coherently processed with internal and external customers.
